
Virtual reality (VR) training has evolved from being a novelty training method that made the Training department look current and cool into a measurable and valuable tool. Across the country, big brands are taking notice and starting to use VR as an efficient, scalable way to train their employees.
In early 2020, PriceWaterhouse Cooper published a study on the effectiveness of VR as a training method specifically focused on soft skills. The results were positive and encouraging. The study found the training was four times faster than regular methods, and trainees were a massive 275 percent more confident in the skills they had learned, and four times more focused. You can’t look at your phone when you’re wearing a VR headset!
VR Training at McDonald’s
In 2020, McDonald’s franchise owners in Louisiana, Texas, New Mexico, Washington, and Iowa started using VR training in their restaurants. The quick-serve restaurant industry is a prime market for VR training, with high levels of staff turnover, a large number of locations, a consistent set of measurable processes, and often an in-restaurant training environment that can be distracting.
The collection of 150-plus stores initially started training their staff on customer hospitality, a soft skill, but one which can be measured in same-store sales. In direct response to the COVID-19 pandemic, they added two new modules: “VR Personal Protective Equipment Training” and “VR Training Drive-Through Training and Mobile Ordering.”
Since January 2020, the system has been deployed in more than 150 restaurants and has been used to train 4,224 crew as of April 2021 The limitations and opportunities the COVID-19 pandemic created lent themselves to VR training. And now VR training is here to stay.
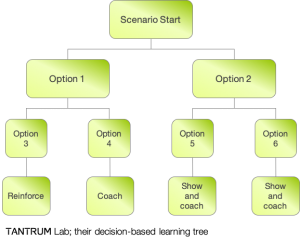
The McDonald’s franchise owners used a decision-based video VR training system where the crew member is faced with a question or problem from a customer. They then have to make a decision in real time on how to answer the customers query. An example of this is a customer coming back into the restaurant from the drive-through. They are upset and tell the crew member they have been waiting outside for their order. The crew member has an immediate decision to make: Get the order ready or apologize and explain that “we should have told you how long it would take” and get the order ASAP. Depending on which option they choose, the customer will react differently, prompting two more unique choices—both with good and bad outcomes. By the end of the scenario, the crew member will experience one of four potential outcomes. If the outcome is excellent, the trainer will reinforce excellent behavior. Good behavior is coached. And poor results are shown the correct choices and given coaching. All of their decisions are measured, scored, and recorded on the client-accessible database.
Mobile Training in Stores
Social distancing is making cluster training a risk that many companies are trying to avoid. If your workforce gathers and a large number become ill with COVID-19, then the businesses’ ability to operate will be compromised. With VR headsets now being self-contained, rechargeable battery-powered units that do not require additional computers or specialist equipment to operate, mobile trainers have the ability to deploy training with consistency in stores. With the training being more focused and immersive, the trainings now can take place in closed restaurant lobbies. And without having to schedule restaurant crews for specific additional shifts, the shorter, focused training modules can be incorporated into a regular shift with minimal distribution to the restaurant’s regular operations. This shift from centralized training locations to mobile training in stores with fully immersive, measurable training is here to stay.
Validation
By connecting these VR training modules to a learning management system (LMS) with an automated confirmation system, each crew member who completes the training is awarded a personalized certificate of completion, along with an e-mail congratulating them. This is an important part of training for crew members. The validation of their effort is key to ensuring that crew member takes their new knowledge onto the floor.
To use VR effectively in training, it is important to:
- Have relatable scenarios
- Provide personalized skills coaching in the VR training
- Use real crew members in the video footage
- Build the training to be highly interactive and decision based
- Have a measurable connected outcome
- Provide validation for the crew
The use of VR training within quick-service restaurants (QSRs) allows store owners to focus on two types of learning: soft skills and hard skills, each with measurable, personalized coaching built in so trainees aren’t just watching a video, they’re part of the process and getting customized feedback on their progress.
In the future, QSRs will be able to use VR training to help develop manager skills, identify future leaders with measured skills tests, roll out new product training systems, and provide hardware training for new restaurant equipment—all done remotely with remote downloads onto the VR headsets in store.
REFERENCES
https://www.pwc.com/us/en/services/consulting/technology/emerging-technology/vr-study-2020.html
https://www.tantrumlab.com/mcdonalds.html




