The Human Resources (HR) function has been habitually criticized for being sluggish and pedantic in terms of its role within the organizational realm. Frustrations abound among disgruntled/dissatisfied employees who see the HR function as the enforcer of leadership’s mandates while being unable/incapable/hapless in alleviating their concerns. The internal discontent/rumblings are routinely amplified through the corporate grapevine, and even positives steps from the leadership are viewed with suspicion. Examples are frequently given in casual conversations about the capabilities of HR functions of other organizations in placating all the key stakeholders and galvanizing initiatives for organizational excellence. Such a “grass is greener on the other side” mindset often erodes morale within the organization and deflates its competitive strengths; this can have serious consequences in trying to keep up with the brutal pace of the digital world.
Consequently, it is becoming increasingly critical for leaders of progressive organizations to enable/facilitate the HR function to respond more quickly and effectively to changing employee expectations, workplace disruptions, and business requirements to stay on par with/ahead of competitors. The case for HR Agility is further reinforced by the following factors:
- Brokering and Discovering Unknown Talent
This reflects the need for skill maximization within the current workforce, which requires keen exploration and active encouragement to help them discover/display their capabilities on a wider bandwidth.
- Building an Adaptive and Ethical Culture
This reflects the entrenchment of core values within the multigenerational workforce as the primary source of employee engagement and value-driven initiatives for a more cohesive workplace.
- Developing a Learning Organization
This reflects the enhancement of capabilities that robustly infuse skills and expertise within the organizational fabric while laying a strong foundation for consistently enriching the knowledge bank.
- Fostering Worker Mobility
This reflects the career optimization for ambitious employees who are committed to expanding their skill sets and accommodating change with a positive frame of mind by proactively adapting to disruptive influences, e.g., proactively aligning their career paths with the inclusion of artificial intelligence-enabled entities in the workplace.
- Applying Science and Fact-Based Analytics
This reflects the refinement of decision-making that comes from adopting a scientific approach coupled with fact-based analytics for taking calculated risks and minimizing the chance of erroneous judgments prone to grave consequences.
Consequently, the following STREAM framework can be used to illuminate the path for enabling and achieving sustainable HR Agility:
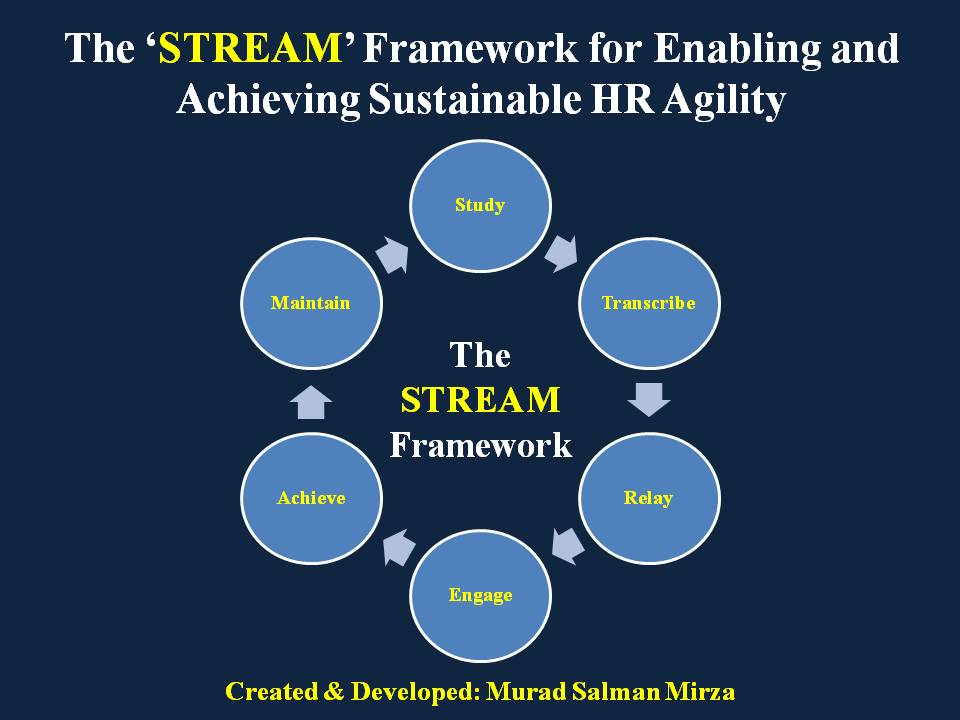
Study (S) Phase
This refers to the deployment of suitable formal and informal means for correctly assessing the issues. For example:

It entails careful collection of authentic data and its meaningful conversion/compilation into viable information that can facilitate thorough analysis for astute decision-making.
Transcribe (T) Phase
This refers to the prioritization of the highlighted issues and associated findings that have come out of the Study Phase. It entails the formulation of desired goals and objectives coupled with the structuring of relevant information into a formal report that has been uniformly formatted in a clear, error-free, and presentable manner for all the key stakeholders to facilitate review and discussion.
Relay (R) Phase
This refers to the communication of the formal report developed during the Transcribe Phase to all the key stakeholders. It entails distribution in an open, transparent, and constructive manner with a cordial invitation for answering any associated questions to create a robust buy-in and develop consensus for desired goals/objectives.
Engage (E) Phase
This refers to the channelization, optimization, and utilization of the required resources to launch appropriate measures/action plans stemming from desired goals/objectives that have been disseminated during the Relay Phase. It entails prudent operational planning with appropriate risk assessment/mitigation measures for gauging the efficacy of available options, selection of a suitable team under capable leadership (if needed), defining key milestones/performance indicators, close coordination/collaboration with all the relevant stakeholders, and associated monitoring mechanisms.
Achieve (A) Phase
This refers to assuring, ensuring, and confirming the attainment of results in congruence with the desired goals/objectives and the operational plans developed during the Engage Phase. It entails timely review of key milestones/performance indicators and taking appropriate corrective/preventive actions to prevent deviation from the desired course of action.
Maintain (M) Phase
This refers to systemizing, sustaining, and refining the whole process with key lessons from the previous phases. It entails an honest self-reflection and a comprehensive review that engenders a solid commitment to consistently improving the client experience of other functions with the HR function. It also includes the timely enrichment of the knowledge bank that is openly accessible to all team members.
Some of the key drivers for the STREAM framework include:
- Robust and unwavering leadership support
- Multichannel and clear communication
- Collaboration and cooperation
- Proactive and meaningful initiatives
- Constructive and insightful feedback
- Efficient and effective resolution
- Consistent and prudent monitoring
- Timely and honest reviews
- Healthy appetite for fruitful improvement
- Innovative mindset for nimbleness, e.g., HR SWAT teams
Parting Insights
HR Agility is an empowerment manifestation that reflects the confidence of corporate leadership in the ability of the HR function to rise above the “noise” of conventionalism and become a recognized strategic partner in organizational success. It does not happen in a vacuum and needs HR professionals to function at a high level of wellbeing and mindfulness as it doesn’t make sense to attach agility expectations to a function that is itself in need of a savior. The digital world is demanding and moves at a brisk pace while routinely leaving behind slacking business concerns that fail to capitalize on HR Agility as a catalyst for transformative success. How agile is your HR?
Murad Salman Mirza is an innovative thinker and an astute practitioner of areas within and associated with the fields of organizational development, talent management, and business transformation. He has lived, studied, and served in different regions of the world, including, the U.S., Australia, South Asia, and the Middle East. His LinkedIn profile can be viewed at: https://www.linkedin.com/in/muradsalmanmirza




